Google’s Gemini App Expands AI Content Verification
The Gemini AI Content Verification feature has recently launched in Google’s Gemini app, enabling users to detect AI-generated content in images, videos, and audio. This groundbreaking tool enhances content authenticity in an era where AI-generated media is becoming increasingly prevalent.
Image Verification Capabilities
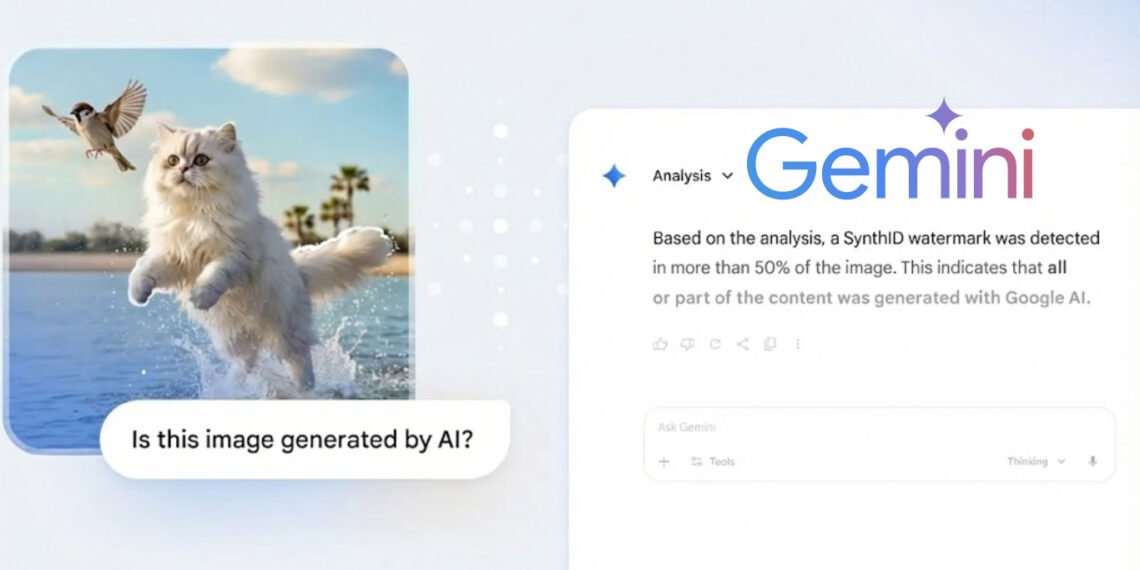
The Gemini app allows users to determine if an image was created or modified using Google AI tools. By simply asking, “Is this AI-generated?”, users can quickly ascertain the origin of the content.
Future Expansion Plans
While the initial release focuses solely on images, Google is planning to extend its verification capabilities to video and audio content in the near future. Additionally, this feature is set to expand beyond the Gemini app, further integrating into Google Search functionalities.
Industry-Wide C2PA Support
In the long run, Google aims to enhance verification by supporting C2PA content credentials, which would facilitate detection of AI-generated media from a variety of sources, including OpenAI’s Sora. Currently, image verification relies on SynthID, Google’s proprietary AI watermarking system.
Challenges in Manual Verification
While manual content verification through Gemini is valuable, the effectiveness of C2PA credentials and watermarking systems like SynthID hinges on social media platforms improving their automatic flagging of AI-generated content. This shift is crucial to reduce the burden on users to verify content authenticity themselves.
1. The Verification Stack: SynthID and C2PA
Content verification relies on a two-pronged technological approach. Google’s current system, SynthID, functions as a robust proprietary watermark. It embeds an imperceptible signal directly into the image’s pixels during the creation process, allowing the Gemini app to later confirm the image originated from Google’s own AI. This method is effective for self-verification but faces limitations outside of the Google ecosystem.
The future of verification rests with the C2PA (Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity) standard. C2PA provides a universal, cryptographic “nutrition label” for all media, tracking its entire history—from when it was captured/created to every edit made. This standard is crucial because it allows users to trust media regardless of the source, and its adoption by major industry players like Adobe, Microsoft, and the BBC is what will ultimately enable automatic flagging across social media platforms, drastically reducing the verification burden on the individual user.
2. The Societal Front: Deepfakes, Scams, and Platform Responsibility
The need for robust AI verification is driven by escalating societal risks. Deepfakes are rapidly moving beyond novelty into serious threats, including sophisticated financial scams and political disinformation campaigns aimed at destabilizing elections. While the Gemini app provides a vital manual defense for individuals, the effectiveness of C2PA hinges entirely on platform compliance.
Social media giants like Meta, X, and TikTok must commit to automatically reading and flagging C2PA credentials upon upload. This is necessary to create a “friction-free” information environment. Furthermore, the constant “arms race” between AI models creating more realistic media and detection systems like SynthID demands continuous investment. If platforms fail to enforce these provenance standards, the speed and scale of deepfake proliferation will quickly outpace the ability of any single app or individual user to verify content authenticity.